For
描述
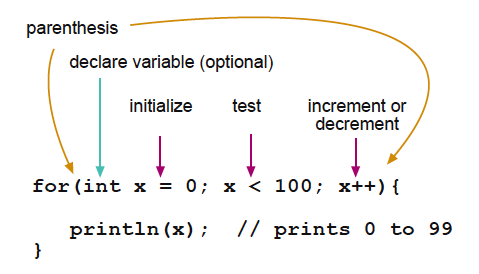
for 語句是用於重複執行在大括號內的一段代碼。通常使用一個增量計數器來增加計數和終止循環。for語句用於重複性操作非常實用,經常和數組結合被用於操作數據或引腳。
for循環語句開頭有3個部分:
for (initialization; condition; increment) {
//statement(s);
}
The initialization happens first and exactly once. Each time through the loop, the condition is tested; if it's true, the statement block, and the increment is executed, then the condition is tested again. When the condition becomes false, the loop ends.
Example
// Dim an LED using a PWM pin
int PWMpin = 10; // LED in series with 470 ohm resistor on pin 10
void setup()
{
// no setup needed
}
void loop()
{
for (int i=0; i <= 255; i++){
analogWrite(PWMpin, i);
delay(10);
}
}
Coding Tips
The C for loop is much more flexible than for loops found in some other computer languages, including BASIC. Any or all of the three header elements may be omitted, although the semicolons are required. Also the statements for initialization, condition, and increment can be any valid C statements with unrelated variables, and use any C datatypes including floats. These types of unusual for statements may provide solutions to some rare programming problems.
For example, using a multiplication in the increment line will generate a logarithmic progression:
for(int x = 2; x < 100; x = x * 1.5){
println(x);
}
Generates: 2,3,4,6,9,13,19,28,42,63,94
Another example, fade an LED up and down with one for loop:
void loop()
{
int x = 1;
for (int i = 0; i > -1; i = i + x){
analogWrite(PWMpin, i);
if (i == 255) x = -1; // switch direction at peak
delay(10);
}
}
更多建議和問題歡迎反饋至 YFRobot論壇