“For”的版本间的差异
来自YFRobotwiki
(以“<font color="orange" size="+1">'''Description'''</font> The for statement is used to repeat a block of statements enclosed in curly braces. An increment counter is ...”为内容创建页面) |
|||
| (未显示1个用户的6个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | <font color="orange" size="+1">'''描述'''</font> | |
| − | + | ||
| + | for 语句是用于重复执行在大括号内的一段代码。通常使用一个增量计数器来增加计数和终止循环。for语句用于重复性操作非常实用,经常和数组结合被用于操作数据或引脚。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | for循环语句开头有3个部分: | ||
<pre style="color:dimgray"> | <pre style="color:dimgray"> | ||
| − | for (initialization; condition; increment) { | + | for (initialization/初始化; condition/条件判断; increment/增量计数) { |
//statement(s); | //statement(s); | ||
| + | //执行语句 | ||
} | } | ||
| 第14行: | 第18行: | ||
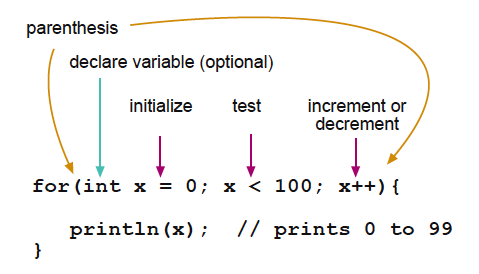
| − | + | [[File:ForLoopIllustrated.png]] | |
| − | <font color="orange" size="+1">''' | + | |
| + | 初始化只在开始执行一次。每次执行一次循环,都会进行一次条件判断;如果为真,则执行括号内语句并增量计数,然后再次条件判断。当条件判断为假时,终止循环。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <font color="orange" size="+1">''' 示例'''</font> | ||
| + | |||
<pre style="color:dimgray"> | <pre style="color:dimgray"> | ||
| 第38行: | 第47行: | ||
| − | <font color="orange" size="+1">''' | + | <font color="orange" size="+1">''' 编码技巧'''</font> |
| − | |||
| − | + | C语言中 for 循环语句 比其他计算机语言中的for语句 更加灵活,其中包括 BASIC。除了分号以外,任何其他3个部分(initialization/初始化、condition/条件判断、increment/增量计数)都可以省略。初始化、条件判断、增量计数可以是任何无关变量的有效C语句,或使用任何C数据类型包括 float。这些各种类型不寻常的for语句可能会解决一些罕见的编程问题。 | |
| + | |||
| + | 例如,使用乘法的增量将生成一个等比数列: | ||
<pre style="color:dimgray"> | <pre style="color:dimgray"> | ||
for(int x = 2; x < 100; x = x * 1.5){ | for(int x = 2; x < 100; x = x * 1.5){ | ||
| − | println(x); | + | println(x); |
} | } | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | 生成: 2,3,4,6,9,13,19,28,42,63,94 | |
| − | + | 另一个示例,使用for循环 使 LED 产生渐亮渐灭的效果: | |
| + | <pre style="color:dimgray"> | ||
void loop() | void loop() | ||
{ | { | ||
2015年8月18日 (二) 22:17的最后版本
描述
for 语句是用于重复执行在大括号内的一段代码。通常使用一个增量计数器来增加计数和终止循环。for语句用于重复性操作非常实用,经常和数组结合被用于操作数据或引脚。
for循环语句开头有3个部分:
for (initialization/初始化; condition/条件判断; increment/增量计数) {
//statement(s);
//执行语句
}
初始化只在开始执行一次。每次执行一次循环,都会进行一次条件判断;如果为真,则执行括号内语句并增量计数,然后再次条件判断。当条件判断为假时,终止循环。
示例
// Dim an LED using a PWM pin
int PWMpin = 10; // LED in series with 470 ohm resistor on pin 10
void setup()
{
// no setup needed
}
void loop()
{
for (int i=0; i <= 255; i++){
analogWrite(PWMpin, i);
delay(10);
}
}
编码技巧
C语言中 for 循环语句 比其他计算机语言中的for语句 更加灵活,其中包括 BASIC。除了分号以外,任何其他3个部分(initialization/初始化、condition/条件判断、increment/增量计数)都可以省略。初始化、条件判断、增量计数可以是任何无关变量的有效C语句,或使用任何C数据类型包括 float。这些各种类型不寻常的for语句可能会解决一些罕见的编程问题。
例如,使用乘法的增量将生成一个等比数列:
for(int x = 2; x < 100; x = x * 1.5){
println(x);
}
生成: 2,3,4,6,9,13,19,28,42,63,94
另一个示例,使用for循环 使 LED 产生渐亮渐灭的效果:
void loop()
{
int x = 1;
for (int i = 0; i > -1; i = i + x){
analogWrite(PWMpin, i);
if (i == 255) x = -1; // switch direction at peak
delay(10);
}
}
更多建议和问题欢迎反馈至 YFRobot论坛